1. try-catch
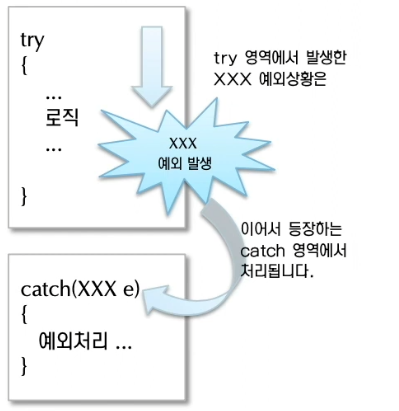
public class Exception {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, b, c;
try {
a = 10;
b = 0;
// 10 나누기 0 → 산술오류 ArithmeticException
c = a / b;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자로 변환할 수 없습니다.");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("클래스가 존재하지 않습니다.");
} catch (Exception e) { // 부모 예외 클래스로 한꺼번에 처리했기 때문에 세세한 예외 클래스 종류는 지금은 알 수는 없다.
System.out.println("NumberFormatException와 ClassNotFoundException 이외에 모르는 어떠한 에러가 발생하였습니다");
}
}
}
1-1. try-catch-finally
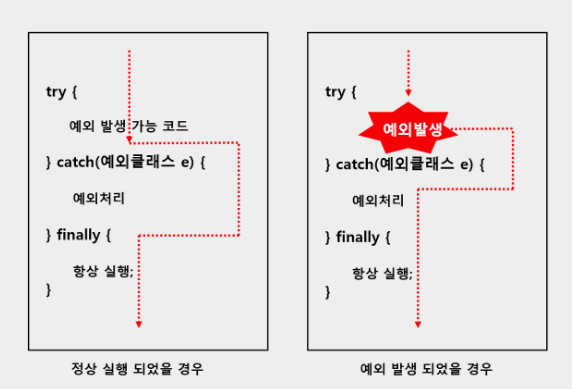
public class Sample {
public void shouldBeRun() {
System.out.println("ok thanks");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample sample = new Sample();
int c;
try {
c = 4 / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
c = -1;
} finally {
sample.shouldBeRun(); // 예외에 상관없이 무조건 수행된다.
}
}
}
2. 예외 던지기 (throw / throws)
1) throw / throws
- throw
- Method 내에서 에러 발생시킬때 사용
- catch로 던진다.
public class myException() {
try {
throw new Excepiton();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("myClass에서 예외 발생");
}
}public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
myException();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("myException에서 예외 발생");
}
}
}- throws
- 상위 메서드로 예외를 던진다.
public class myException() {
throw new Exception();
}public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
myException();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("myClass에서 예외 발생");
}
}
}
💡 Reference
07-04 예외 처리
프로그램을 만들다 보면 수없이 많은 예외 상황이 발생한다. 물론 예외가 발생하는 것은 프로그램이 오동작을 하지 않게 하기 위한 자바의 배려이다. 하지만 이러한 예외 상황을 무시하…
wikidocs.net
728x90
반응형
'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] OOP (Object Oriented Programming) (0) | 2024.05.28 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 기본함수 (0) | 2024.05.28 |
| [Java] 조건문 & 반복문 (0) | 2024.05.28 |
| [Java] 문법 (0) | 2024.05.28 |
| [Java] 기초 (0) | 2024.05.28 |